1MG FlippingBooks
Our agricultural future will be defined by Science and Innovation
Prof. Victor Sadras is a world authority on crop ecophysiology with an interest in the adaptation of crops to environmental stresses, including water deficit, extreme temperatures, nutrient deficit, soil physical and chemical constraints, pathogens and insects. He leads the team of Crop Ecophysiology at the South Australian Research & Development Institute (SARDI). Prof Sadras has distilled the background, objectives and findings in his co-authored paper Making Science More Effective for Agriculture published in the international journal “Advances in Agronomy”, Volume 163, 2020.
Making science more effective for agriculture
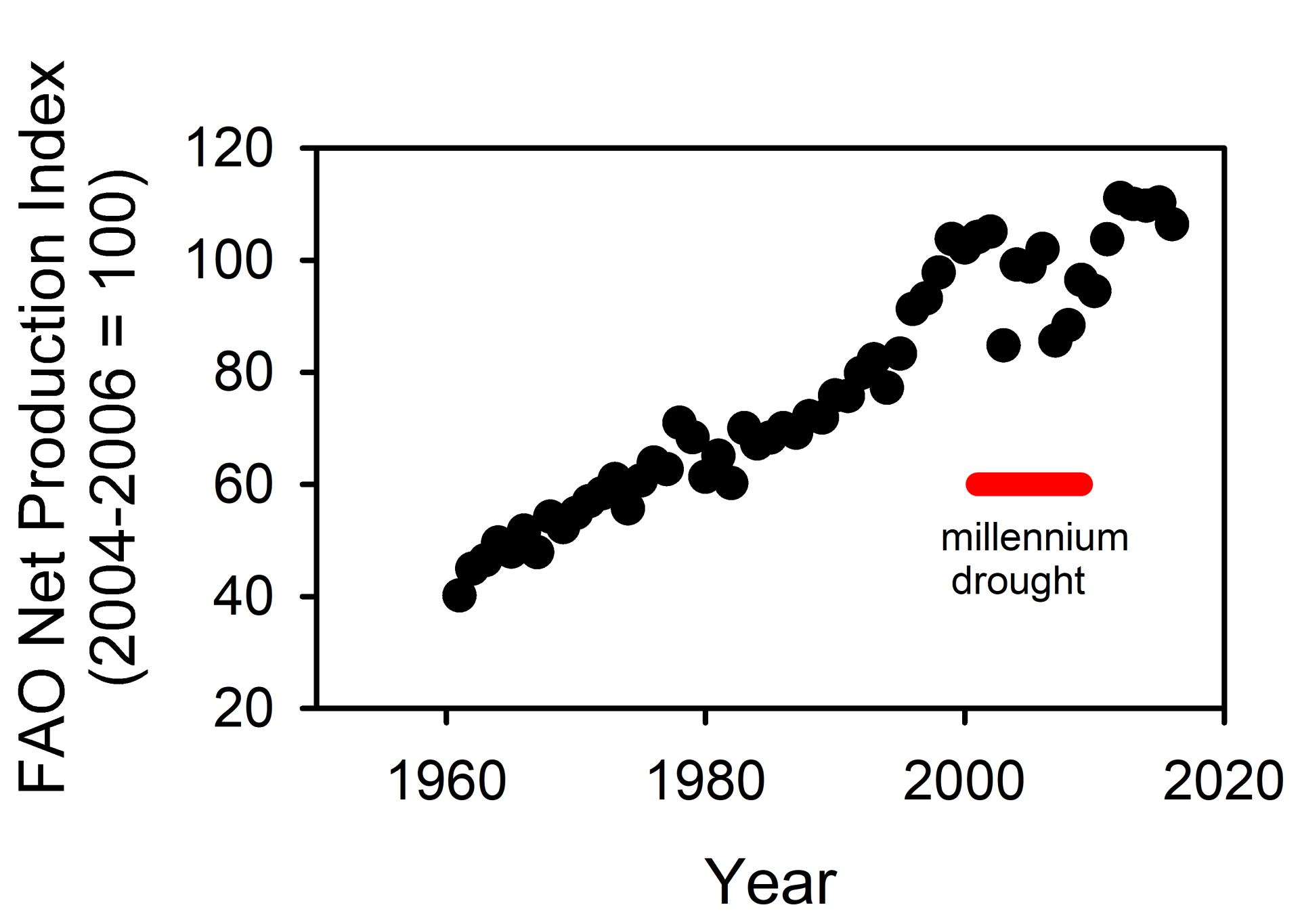
Australian agricultural output increased 2.8-fold since 1961, a growth trajectory only disrupted transiently by the widespread, persistent and severe millennium drought. Innovative producers engaged with an effective scientific community underlie this outstanding trajectory. The evidence is clear – investment in agricultural research and development (R&D) is highly profitable for Australian agriculture; returns on investment are 10:1 and often much higher; few investments elsewhere in the economy are more profitable.
A group of scientists, breeders, economists, farmers, managers and industry representatives met in Adelaide to pose questions about effective investment in agriculture R&D. Acknowledging Australia’s already high return on investment record historically, the meeting asked: “can we do better?”. Despite a compelling case for more investment, we see less. In many countries, especially the high-income countries like the United States and Australia, public investment in agricultural R&D has stagnated or is declining in real terms. At the same time, funding is occasionally misallocated to fashionable R&D programs with unlikely payoffs. Additional concerns are many and varied including: (1) a shift towards bureaucratic industrial principles to organise scientific work; (2) the opportunity cost of the scientists’ time for applying and managing funds; (3) reduced scope to pursue the unexpected because of contractual constrictions, incentive structures, and restricted exchange of information between scientists; (4) and the erosion of scientific expertise in core disciplines including crop science and ecology.
The core issue is to manage the tension between the fact that we cannot plan for the discovery of the unknown, but in agriculture, we cannot afford expensive distractions – nitrogen fixing cereals, for example, are an expensive distraction. Julian Alston, an Australian economist that pioneered economic approaches for allocation of limited resources to R&D, formalises this tension:
“ …There is a demonstrated need for formal economic evaluation of alternative investments and priority-setting procedures but … formal evaluation and priority-setting procedures should not be used as a basis for replacing ingenuity, serendipity and scientific entrepreneurship with bureaucratic procedures…”
Data-driven technologies, including “omics” and precision agriculture have overpromised and under-delivered. They share an emphasis on data (“we measure stuff because we can”). Big data is the next promise. The question must be asked: “To what extent are we limited by data, and to what extent by our understanding of the problem at hand”. Chief Research Scientist at the Division of Plant Industry, CSIRO, Dr John Passioura noted:
“…major technological innovations have major consequences. Their inventors often develop them to solve problems that are otherwise intractable – such are their motives. However, as the appreciation of the power of these technologies spreads, fascination with them can change their role. They become seen as powerful tools to try in all sorts of novel ways. They may then become the (often inept) drivers of research, rather than the means to solve specific important problems…”
The meeting in Adelaide concluded:
“…there is no silver bullet in agricultural R&D. Agricultural innovation emerges from new combinations of existing technologies. Funding bodies should scrutinise carefully new ’bandwagons‘. Donors and investors who are reluctant to support ’more of the same‘ unintentionally favour spurious claims of breakthroughs that need to be challenged. Excessive emphasis on data clouds the issues, whilst testable hypotheses remain paramount for robust and relevant science. …the situation is not static – the targets of agricultural R&D evolve. A likely future direction for R&D in agriculture and food will be to ask as much about the efficiency of demand issues as the past has been concerned with food supply. Environmental resilience is expected to remain central, and the interface between agriculture, human nutrition, diet and obesity is increasingly important. Irrespective of the targets, investments in agricultural science and technology must be used more effectively, and declining public investment reversed. All actors must preserve the same high, evidence-based standards that has led to realised success – but also be prepared to move out of their intellectual comfort zones.”
EDITOR’S CONCLUSIONS:
1MG commissioned this piece originally from the outstanding Queensland Alliance for Agriculture and Food Innovation (QAAFI), where one of Professor Sadras’ co-authors Professor Daniel Rodriguez works as a Professional Research Fellow in the Centre for Crop Science. QAAFI is yet another of Australia’s many vanguard research institutes ultimately serving our country’s farmers and the wider agricultural economy. We love their phrase about “ingenuity, serendipity and scientific entrepreneurship” because it describes not only scientists but also our innovative farmers. Australian farmers have always exhibited creativity and experimentation in many ways, and this should grow. Yes, government does need to increase R&D funding in agriculture, and do it well and knowingly. Farmers ought be more vocal about this subject with their local MPs, or direct to the Minister, at State or Federal levels. As publishers on the need for more science and innovation in our society, we feel passionately about this. And we are experienced enough to know that if we don’t call out for it, define it , take a stand, the results will be lesser, or nil. Agricultural peak bodies also ought to lobby aggressively for this – many are already. The pace should increase. Rigorous science and innovation are critical to Australia’s farmers –at the farm, regional, state and federal government levels, all. No food producing nation will grow its returns over the years to come without the fulcrum of intelligently applied science and innovation. Such intelligent decisions can only be arrived at through greater interaction between farmers, scientists and government. And every farmer worthy of the name should grow in the Australian tradition of self–education, experimentation and now more than ever – engagement and collaboration. Our collective agricultural voice ought be heard at government, and research priorities, key concerns for both SARDI and QAAFI, be refined, indeed defined, by the end beneficiary: our farmers.
















